
Palay and Corn production for the 4th quarter of 2024 are vital indicators of the agricultural sector's health and sustainability in the province. This report outlines key trends, challenges, and factors influencing production, offering insights into both the positive and negative impacts on crop yields. The effects of recent typhoons have significantly contributed to a decrease in production compared to previous quarters. By providing accurate and timely data, this report aims to guide policy decisions, improve agricultural strategies, and equip stakeholders—such as farmers, policymakers, and industry leaders—with the necessary tools to address the evolving challenges of the agriculture sector.
The total palay production in Quirino Province for the 4th quarter of 2024, as shown in Table 1, experienced a decrease, falling from 47,060.69 metric tons (mt) in 2023 to 38,633 mt. The area harvested decreased from 10,769 hectares in 2023 to 9,535 hectares in 2024 due to a movement of harvest to Quarter 1 of 2025.
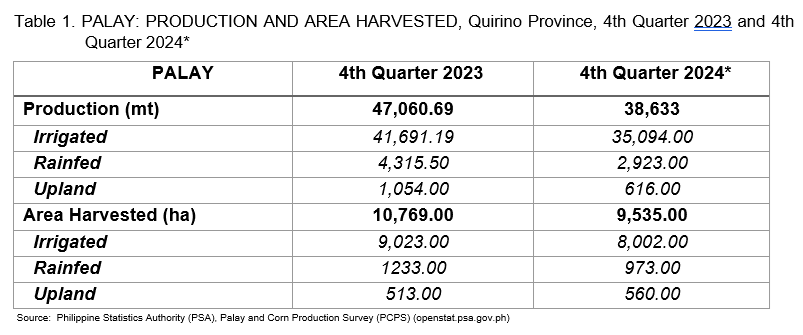
The production across different ecosystems showed a decline in all production categories: irrigated production dropped from 41,691.19 mt to 35,094 mt, rainfed production decreased from 4,315.50 mt to 2,923 mt, and upland production fell from 1,054 mt to 616 mt. These reductions were primarily caused by damage from Typhoons Kristine, Nika, and Pepito, as well as continuous heavy rainfall, which led to flash floods and lodging that affected the plants during the maturity stage, as shown in Figure 1.
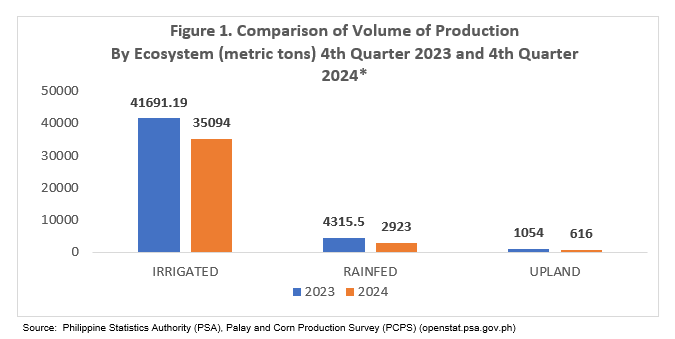
The area harvested from different ecosystems showed a reduction, with the largest decline observed in irrigated areas, which dropped from 9,023 hectares in 2023 to 8,002 hectares in 2024. Rainfed areas decreased from 1,233 hectares to 973 hectares, while upland areas saw a slight increase, rising from 513 hectares in 2023 to 560 hectares in 2024. This decrease in the area harvested was partly due to the movement of some harvests to the first quarter of 2025, as shown in Figure 2.
In the 4th quarter of 2024, Quirino Province experienced an increase in corn production, rising from 46,662 metric tons (mt) in 2023 to 54,111 mt. The area harvested for corn also grew, from 10,976 hectares in 2023 to 12,682 hectares in 2024, due to a significant water supply as well as continuous rainfall, as shown in Table 2.
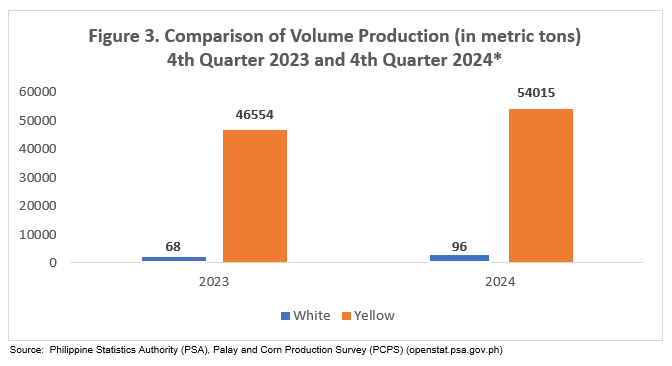
Quirino Province experienced an increase in corn production for 4th Quarter 2024. This growth was primarily driven by a significant rise in yellow corn production, which increased from 46,554 mt to 54,015 mt, while white corn production rose from 68 mt to 96 mt. The rise in production was attributed to a larger area planted and bigger cob sizes, resulting from sufficient rainfall and the use of high-quality seeds, as shown in Figure 3.
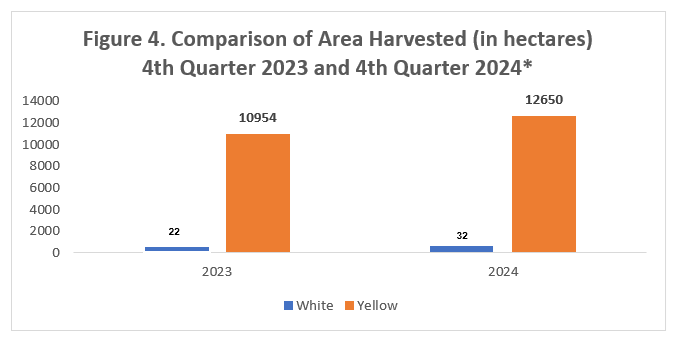
The area harvested for yellow corn increased from 10,954 hectares to 12,650 hectares, while the area harvested for white corn grew from 68 hectares in 2023 to 96 hectares in 2024. Both benefited from an adequate water supply due to rainfall, as shown in Figure 4.
Definitions of Terms
Crop Production - This refers to quantity produced and actually harvested during the reference period. It includes those harvested but damaged, stolen, given away, consumed, given as harvesters’ and threshers’ shares, reserved, etc. Palay production from seed growers which are intended for seed purposes is excluded from the survey.
Area harvested – This refers to the total area harvested to palay during the reference quarter. It may be less than or equal to the total area planted to palay.
Irrigated - Area with irrigation facilities supplying water through artificial means like gravity, force/power, pump, etc. Irrigated area become rainfed only, when the irrigation system is no longer operational for the past two (2) years and beyond repair and there is no plan of irrigating the farm.
Rainfed - The area holds standing water but solely dependent on rainfall for its water supply. It may have dikes that retain rainwater.
Upland - Farm land which has no amenities to hold for standing water. It is usually located along elevated lands, along rivers, between hills, hillsides, etc.
White Corn - Used primarily for human consumption.
Yellow Corn - Generally used as feed grain which includes all type of corn other than white.
Approved for Release:
ENGR. CHERRY GRACE D. AGUSTIN
Chief Statistical Specialist
